Attackers often steal passwords from social networks, online banking sites, and online stores. Google has developed a special service to protect user data. It works only in Chrome. The service checks data from sites against a common database of stolen usernames and passwords, and then informs users if their data is on the list.
Why the warning appears
Starting from version 79, Google Chrome has included a system to warn you about stolen passwords. It works in the following way:
- When logging in to the site, a hashed copy of user data is created and sent to Google.
- On Google’s servers, the data is decrypted using PSI and k-anonymity technology and then compared with the database of compromised usernames and passwords.
- If a username and password are found in that database, the user receives an appropriate message.
The service can be disabled in the browser settings. Go to the chrome://settings/security page and flip the “Warn you if passwords are exposed in a data breach” switch off.
What to do
If a password is compromised by a data breach, you need to log in to the site and change your login details in your personal account. We also recommend that you check your computer and mobile devices for viruses.
How to check for compromised passwords
On computer
- open the menu (three dots in the top right corner),
- go to Settings,
- select Autofill from the left sidebar,
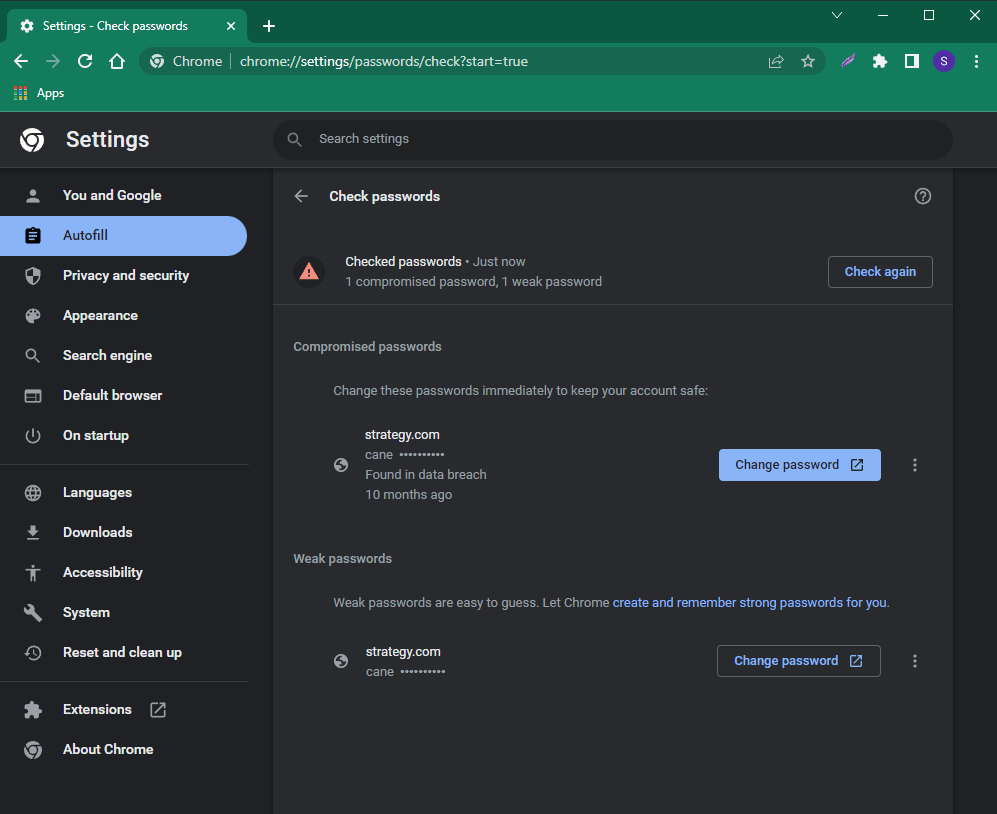
- proceed to the Password manager and click Check passwords.
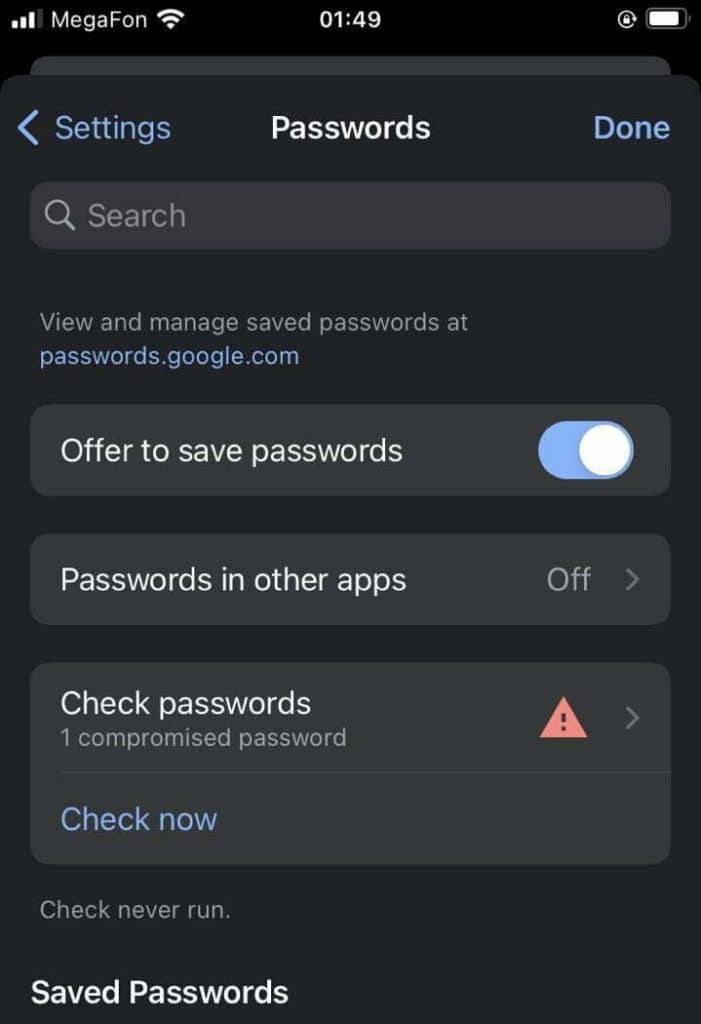
On phone or tablet
- open the menu (three dots in the corner),
- go to Settings,
- proceed to the Passwords section,
- tap Check passwords or Check now.
Once checked, the sites whose data has been stolen will appear in the list.
When you click on a compromised account, the browser will automatically redirect you to a site to change the password. You’ll need to log in and change your login information in your account settings.
At times, Chrome will report that passwords have been compromised when a user logs in through the same browser on a different device. The system perceives this as data theft because the parameters and IP addresses of the two gadgets don’t match. In this case, there is no need to change the password.
Improving security
To avoid regularly encountering messages about cracked passwords, you should follow basic security rules when surfing the Internet:
- Create different passwords for different sites and social networks.
- Use upper and lower case letters, numbers and additional symbols in passwords.
- Carefully check the domain of the site before entering the data for authorization.
It is also recommended to keep your browser and operating system up-to-date.